Spotlights
International Sales Manager, Global Account Manager, Export Coordinator, International Trade Specialist, International Marketing Manager, Foreign Market Analyst, Export Compliance Officer, International Trade Consultant
Ever heard the term Gross Domestic Product or GDP? GDP is the total value of everything a country produces in a year. Almost 11% of America’s entire GDP comes from exports—goods and services we sell to other countries!
Export Sales Representatives are a vital part of that sales process. They serve as the bridge between manufacturers and overseas buyers, ensuring that products made in America find their way into global markets. It’s a dynamic career that combines the thrill of sales, the fun of travel, and the art of international diplomacy.
If you have a flair for communication, a knack for negotiations, and a curiosity about global markets, this might be the perfect career field for you!
- Exploring new countries and cultures
- Creating relationships with international clients and partners
- Mastering negotiation skills, understanding global markets, and contributing to a company’s international success
Working Schedule
- Export Sales Representatives work full-time with frequent travel required, causing them to be away from home some nights, weekends, or holidays.
Typical Duties
- Learn all the details about various products/services to be sold
- Understand and try to meet sales quotas
- Find prospective customers by using business listings and references
- Attend international trade fairs and conventions to gain exposure
- Participate in membership organizations to network and generate leads
- Connect with clients and prospects to gauge their requirements
- Schedule product or service demonstrations. Explain features and benefits
- Deliver technical presentations to potential buyers and other interested parties
- Share product samples and brochures
- Address inquiries about products, costs, stock, and payment options
- Assist clients in choosing products that align with their needs. Discuss customization of products/services when applicable
- Provide price estimates, contract conditions, information about guarantees, warranties, and discounts or promotions. Negotiate prices, terms, and conditions
- Offer estimated delivery dates and times
- Draft sales agreements and order documents. Finalize contract specifics and payment arrangements
- Gather and review credit data on potential clients
- Prepare and forward sales agreements to applicable departments for further action
- Send orders to production companies, or buy goods from producers or brokers and distribute to wholesale and retail customers
- Coordinate with logistics and shipping teams to ensure timely, compliant deliveries and setup
- Prepare shipping documents (if requested by customs department)
- Engage with clients post-sale to offer follow-up support and address any concerns
- Offer advice to retailers about product placement and marketing ideas
Additional Responsibilities
- Respond to emails, website contact forms, and phone calls
- Utilize customer relationship management tools
- Stay in touch with existing customers to promote and market new items or renew orders. Ensure customers have copies of catalogs or samples
- Train other sales reps
- Maintain records of travel and expenses; submit vouchers for reimbursement
- Keep travel documentation updated, such as passport and visas
- Keep up-to-date on market trends, new products, competitor offerings, and pricing. Share and discuss insights with peers regarding sales techniques
- Stay informed about international regulations and restrictions
- Manage records, sales reports, and expense tracking
- Monitor inventory levels and reorder products, if needed
- Help to resolve customs-related issues, and ensure products meet the regulatory standards of the importing country
- Collaborate with finance departments to manage foreign currency transactions
- Assess current challenges and look for new opportunities in overseas markets
Soft Skills
- Accuracy
- Active listening
- Analytical
- Attention to detail
- Business acumen
- Communication skills
- Confidence
- Customer service
- Decisiveness
- Detail-oriented
- Email and phone etiquette
- Emotional intelligence
- Empathy
- Flexibility
- Independent
- Integrity
- Interpersonal skills
- Motivation
- Patience
- Persistence
- Persuasiveness
- Problem-solving skills
- Storytelling
- Teamwork
Technical Skills
- Knowledge of software programs for:
- Accounting
- Business intelligence
- Calendaring
- Cloud-based management
- Customer relationship management
- Database management
- Datamining
- Enterprise resource planning
- Financial analysis
- Presentations
- Project management
- Sales and marketing
- Spreadsheets
- Trade management
- Transaction security
- Travel arrangements
- Videoconferencing
- Technical expertise in the products and services being sold
- Understanding of product compliance with foreign standards
- Ability to analyze international market trends
- Familiarity with international trade regulations, tariff codes, and customs procedures
- Knowledge of export documentation and shipping logistics
- Understanding of currency exchange and international banking practices
- Fluency in target country languages
- Agriculture and food producers
- Apparel and fashion brands
- Commodity traders
- Exporting houses
- Manufacturing companies
- Multinational corporations
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Technology firms
- Trading companies
- Wholesale distributors
Export Sales Representatives often travel to different countries, where they must know how to properly engage with the local cultures and customs. They must navigate language barriers, manage time zone differences for meetings, and adhere to international regulations, all while hitting sales targets in foreign markets.
Sometimes the financial stakes are high and there can be a lot of pressure from employers for sales reps to close deals. Meanwhile, irregular work hours can cause hardships for workers with families, making it tough to maintain a balanced work-life equilibrium. In addition, the frequent travel routine requires workers to adapt to diverse climates and manage health risks, as well.
Exports are a major part of our economy, with America’s top exports including items such as machinery (including computers), aircraft, vehicles, electrical equipment, medical apparatus, pharmaceuticals, precious metals, cereals, oil seeds, meat, and cotton, among others.
These days companies in virtually every industry are selling to global customers. Even small businesses can tap into worldwide markets, especially thanks to the convenience of online shopping.
Many exporters are striving to ensure that international workers are being treated better, requiring fair standards and practices as part of any trade agreements. Some deals, like the USMCA in North America, make trading simpler and help local economies. However, any international trade comes with its share of supporters and critics.
Salespersons in general often love to talk, share ideas, and collaborate with others to get things done. Export Sales Reps may have been keen to travel and curious about other countries and cultures. They might have also had an independent streak, wanting to find a job where they had some freedom and were entrusted to work without being micromanaged.
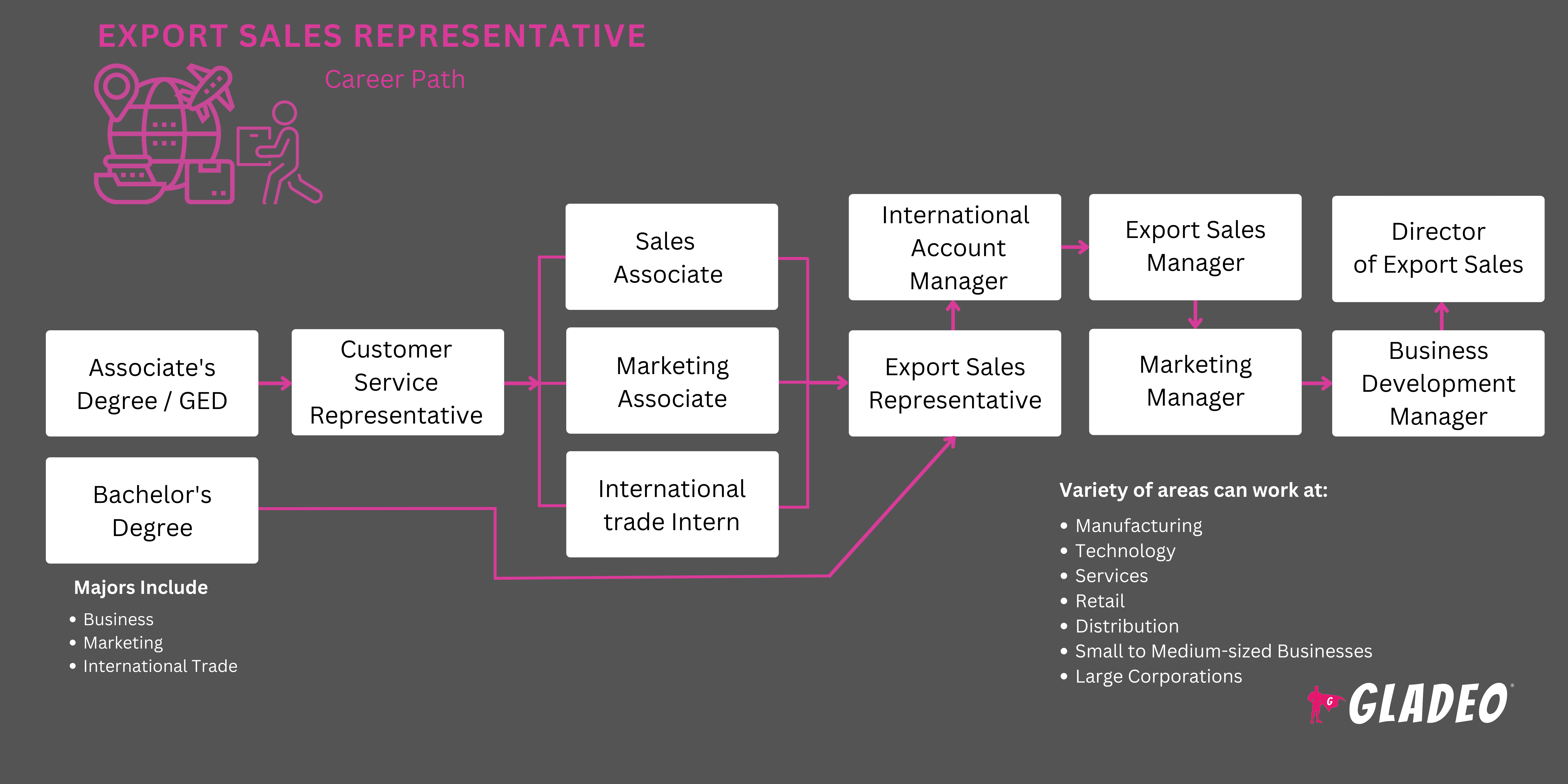
- Export Sales Representatives need at least a high school diploma or equivalent
- The majority of reps have a bachelor’s or, in some cases, a master’s degree
- Those selling nontechnical or nonscientific products may not need a degree, but a bachelor’s in business, international business, marketing, accounting, or a related area can enhance prospects
- Representatives selling scientific and technical products usually need a related bachelor’s
- Large multinational corporations may prefer or require candidates to have at least a bachelor’s
- Common undergraduate courses include:
- Cross-cultural communication
- Emerging markets and business strategies
- Foreign exchange
- Global marketing strategies
- Global supply chain management
- International business law and ethics
- International business negotiations
- International economics
- International risk management
- International trade and policy
- Some companies offer formal training programs featuring technical instruction followed by supervised on-the-job training
- Certifications include:
- Certified Exporter
- Certified International Trade Documentation Specialist
- Certified International Trade Manager
- Certified International Trade Marketing Specialist
- Certified International Trade Professional
- Certified U.S. Export Compliance Officer
- Manufacturers’ Representatives Educational Research Foundation - Certified Professional Manufacturers’ Representative and Certified Sales Professional
- Institute of Hazardous Materials Management - Certified Dangerous Goods Professional
- Look for accredited colleges offering majors in business, international business, marketing, or accounting.
- If planning to sell technical products or services, you may need a degree in an applicable field
- Engineering college programs should be accredited by ABET
- Seek programs with internships or opportunities to get practical experience
- Check out their current research and research facilities
- Compare tuition and fees costs, noting in-state vs. out-of-state costs
- Review scholarship and financial aid options
- Check out graduation and job placement statistics for alumni
- In high school, you’ll need to master a lot of subjects, including business, international business, marketing, economics, and social sciences
- To hone your sales skills, take English, writing, speech, debate, and foreign languages
- If planning to sell technical products, sign up for plenty of math, science, engineering, and technology courses in high school
- Try to pin down what regions or export products/services you’re interested in!
- Apply for part-time sales-related jobs, especially if they have export departments
- Polish your phone etiquette and powers of persuasion
- Volunteer to serve on school committees. Help with extracurricular activities, with a focus on roles that offer leadership and management experiences
- Take online courses via edX or Udemy to polish up your sales and marketing skills
- Call a few manufacturers to ask if you could shadow a salesperson for a day
- Read academic articles and watch documentary videos related to international business and trade
- Familiarize yourself with current global events and trade developments
- Participate in relevant online forums and discussion groups
- Keep track of all your work and academic accomplishments for your resume and/or college applications
- Join professional organizations to network, learn, and have fun!
- Scan job portals like Indeed.com, Glassdoor, ZipRecruiter, USAJOBS, and other sites
- If you don’t have much sales experience, you might want to focus on landing a sales job or an internship first
- Know the sales lingo and best practices for finding leads, negotiating good deals, closing deals, and maintaining strong customer relationships
- Make a profile on LinkedIn and other networking platforms
- Review job ads and look for keywords to list on your resume. Also cite quantifiable results (such as total dollar amounts of products sold), when possible
- Stay connected to your professional network and ask for leads on upcoming job openings
- Keep up-to-date on the latest developments related to the product or service type you want to sell
- Ask previous professors and supervisors to write recommendation letters or request their consent (in advance) to list them as references
- Do your research on potential employers. Learn what kind of products and services they manufacture or sell and who their target buyers are
- During interviews, demonstrate a keen awareness of trends in the industry
- Review Export Sales Representative resume templates and sample interview questions
- Conduct mock interviews with friends or your school’s career center
- Dress appropriately for job interviews.
- The best way for a sales rep to move up is to make sales! When you’re making money for your employer, they notice!
- Consistently find great leads, negotiate great deals—and close as many high-paying sales as you can. Try to exceed your quotas
- Keep in mind, many sales jobs pay a salary plus commission, i.e. “money a salesperson earns based on the number of sales they have made.”
- Commissions are a major financial incentive used to motivate sales reps and reward them for great jobs. So “climbing up the ladder” doesn’t have to mean “getting a promotion”—it could mean bringing in bigger commissions and getting a chance to sell to larger clients
- Let your supervisor know you are interested in advancement. Offer to take the lead on tough projects or trips that maybe other sales reps don’t want to go on
- Knock out additional education and training to improve your ability to make sales
- If there is a manufacturer-specific certification for the items you sell, get it!
- If you focus on a particular country, learn the language!
- Watch or listen to demos to stay fresh
- Treat everyone with respect, be on time and well-prepared for presentations, offer solutions, and stay focused on maintaining long-term customer relationships
- Keep growing your professional network and making deep connections with major buyers
- Stay active in professional engineering organizations, attend conferences and workshops, and offer to give lectures
- Stay current on regulatory changes to ensure your organization is always compliant
Websites
- Agricultural Trade Promotion Program
- District Export Council
- Emerging Markets Program
- EXIM
- Export Credit Guarantee Program
- Foreign Agricultural Service
- Foreign Commercial Service
- Foreign Market Development Program
- Institute of Hazardous Materials Management
- International Trade Administration
- International Trade Certification
- Manufacturers’ Representatives Educational Research Foundation
- Market Access Program
- National Association of Sales Professionals
- National Association of Women Sales Professionals
- National Customs Brokers & Freight Forwarders Association
- National Sales Network
- North American Association of Sales Engineers
- Office of International Trade
- Sales and Marketing Executives International
- Sales Management Association
- Small Business Development Centers
- State Trade Export Program
- Strategic Account Management Association
- US Commercial Service
- US Export Assistance Centers
- US Small Business Administration
- US Trade and Development Agency
Books
- Building an Import/Export Business, by Kenneth Weiss
- Export/Import Procedures and Documentation, by Thomas E. Johnson and Donna L. Bade
- Mastering Import & Export Management, by Thomas Cook and Kelly Raia
The job of an Export Sales Representative can be rewarding in many ways, but it’s also demanding. For some, the travel schedule simply isn’t suited to their lifestyle. If you’re interested in exploring some related occupations, check out the suggestions below!
- Advertising Sales Agent
- Customer Service Representative
- Insurance Sales Agent
- Public Relations Specialist
- Purchasing Managers, Buyers, and Purchasing Agent
- Real Estate Broker and Sales Agent
- Retail Sales Worker
- Sales Engineer
- Sales Manager
- Securities, Commodities, and Financial Services Sales Agent
- Wholesale and Manufacturing Sales Representative
Newsfeed
Featured Jobs

Online Courses and Tools

Annual Salary Expectations
New workers start around $48K. Median pay is $65K per year. Highly experienced workers can earn around $96K.






